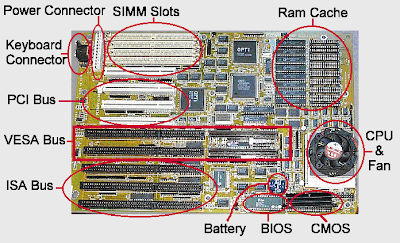
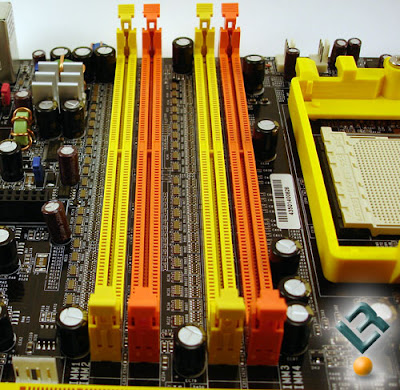
Power Connectors:-
The motherboard has a socket to attach the power cables coming from the power supply. ATX form factor motherboards and power supplies use a single 20-wire motherboard power cable. All others use a pair or 6-wire cables.
The cables are connected to the motherboard so that the black wires are together in the middle. This connector is usually found near the back right-hand side of the motherboard, near the power supply.
Voltage Regulators:-
In old days, devices used to run on same voltage of 5V. The arrival if processors and other devices running at different voltages led to the necessity of motherboards. These regulators reduce the 5V signal to those voltages typically needed by processors: 3.3V or lower.
Processor manufacturers fit in a dual voltage scheme into their latest designs. The processor is fed two voltages: the external or "I/O" voltage is typically 3.3V, while the internal or "core" voltage is lower: usually 2.8 to 3.2 volts. The voltage regulator is responsible for generating the correct voltage for the processor.
The voltage regulator can normally be identified by the large heat-sinks that are placed on it; Voltage conversion generates a great deal of heat. On many motherboards, the cooling level of the entire system case is important to ensure that the voltage regulators are cooled satisfactorily. Overheating regulators can cause lockups and other problems.
The motherboard has a socket to attach the power cables coming from the power supply. ATX form factor motherboards and power supplies use a single 20-wire motherboard power cable. All others use a pair or 6-wire cables.
The cables are connected to the motherboard so that the black wires are together in the middle. This connector is usually found near the back right-hand side of the motherboard, near the power supply.
Voltage Regulators:-
In old days, devices used to run on same voltage of 5V. The arrival if processors and other devices running at different voltages led to the necessity of motherboards. These regulators reduce the 5V signal to those voltages typically needed by processors: 3.3V or lower.
Processor manufacturers fit in a dual voltage scheme into their latest designs. The processor is fed two voltages: the external or "I/O" voltage is typically 3.3V, while the internal or "core" voltage is lower: usually 2.8 to 3.2 volts. The voltage regulator is responsible for generating the correct voltage for the processor.
The voltage regulator can normally be identified by the large heat-sinks that are placed on it; Voltage conversion generates a great deal of heat. On many motherboards, the cooling level of the entire system case is important to ensure that the voltage regulators are cooled satisfactorily. Overheating regulators can cause lockups and other problems.